Cryptocurrency has emerged as a revolutionary financial system, but at the heart of it lies an even more groundbreaking technology—blockchain. For many, the terms “blockchain” and “cryptocurrency” are interchangeable, but they are not quite the same. Blockchain serves as the foundational technology that makes cryptocurrency possible. In this blog, we’ll explore what blockchain is, how it works, and why it plays such a critical role in the crypto ecosystem.
Understanding Blockchain Technology
What is Blockchain?
To put it simply, blockchain is a type of digital ledger that records transactions in a secure, transparent, and decentralized way. Each record, or “block,” is added to the chain after being validated by multiple participants in a network, ensuring that no single entity controls the ledger.
Blockchain’s true innovation lies in its decentralized nature. Unlike traditional systems where banks or financial institutions act as intermediaries, blockchain operates without a central authority. This lack of central control not only makes transactions faster and cheaper but also ensures a higher level of security and transparency.
How Blockchain Works
So, how exactly does blockchain work? Think of blockchain as a continuously growing list of records, each of which is linked and secured through cryptography. Here’s a simplified breakdown:
- Transaction is Requested: When someone initiates a transaction (buying or selling crypto, for example), the request is sent out to the blockchain network.
- Validation by Nodes: These transactions aren’t approved by a central entity. Instead, they’re validated by a distributed network of computers, called “nodes.” Each node holds a copy of the entire blockchain and ensures the transaction follows the rules.
- Added to a Block: Once validated, the transaction is grouped with others into a “block.”
- Block is Chained: The block is then cryptographically linked to the previous block, creating a continuous chain that can’t be altered or deleted.
This process makes blockchain a highly secure system, as altering any part of the chain would require changing all subsequent blocks, something nearly impossible to achieve.
Why Blockchain is Essential to Cryptocurrency
Decentralization in Crypto
One of blockchain’s greatest strengths is its decentralized nature. In traditional financial systems, intermediaries like banks or payment processors are required to verify transactions. These institutions not only have control over the flow of money but also charge fees and impose rules on how funds are managed.
Blockchain, by contrast, operates without the need for intermediaries. It allows direct peer-to-peer transactions that are verified by the network itself. This is one of the key reasons why cryptocurrency has become such a disruptive force in the world of finance. No central authority can manipulate the currency or restrict its use, making it a truly global and democratic financial system.
Transparency and Trust
Blockchain fosters a new level of transparency in the crypto space. Every transaction made on a blockchain is recorded and can be viewed by anyone. Although the details of the parties involved are anonymized, the record of the transaction itself is public. This creates a trustless system, meaning users don’t have to rely on trust in a central authority or each other—trust is placed in the technology itself.
For example, Bitcoin’s blockchain is a public ledger where every Bitcoin transaction ever made can be traced back. This transparency prevents fraud, builds trust in the system, and provides a verifiable record for all to see.
Immutability
One of the most important features of blockchain is its immutability, meaning that once data is recorded on the blockchain, it cannot be altered. Each block is cryptographically linked to the previous one, creating an irreversible chain of transactions.
This is crucial for the integrity of cryptocurrency transactions. Unlike traditional financial systems where records can be altered or tampered with, blockchain’s immutability ensures that once a transaction is validated and added to the chain, it is permanent. This makes blockchain incredibly reliable for both financial transactions and record-keeping.
Key Benefits of Blockchain in Crypto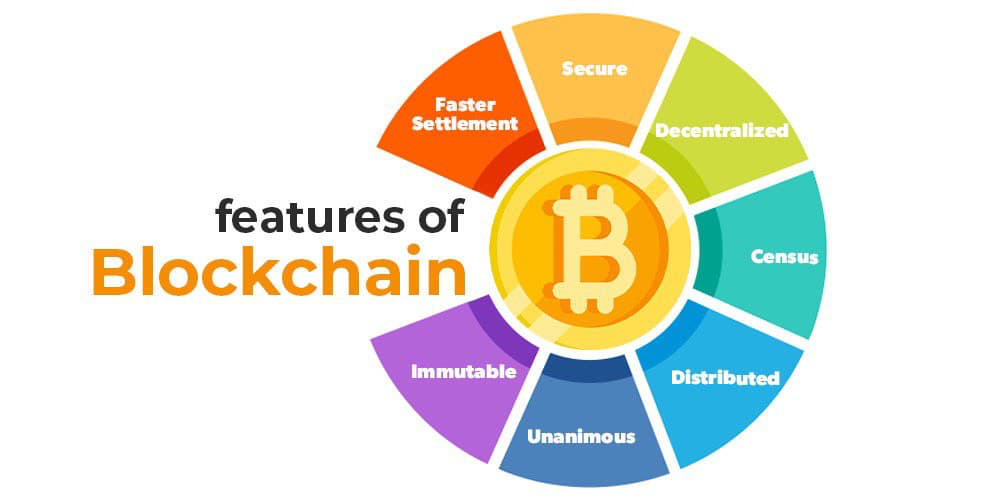
Security and Encryption
In the digital world, security is paramount, especially when it comes to handling money. Blockchain’s security features make it particularly well-suited for cryptocurrency. Every transaction is encrypted and linked to the previous one, making it extremely difficult for hackers to manipulate the data.
Additionally, blockchain networks are decentralized, meaning there is no single point of failure. Unlike traditional centralized systems, where one breach can compromise an entire database, blockchain’s distributed nature means that even if one part of the network is compromised, the rest remains secure.
Anonymity and Privacy
While blockchain is transparent in recording transactions, it also protects the identities of those involved. In the context of cryptocurrency, users’ personal details are not tied to their transactions. Instead, they are represented by alphanumeric addresses, ensuring a degree of privacy.
However, it’s important to note that this level of anonymity varies across different blockchains. For instance, Bitcoin is often referred to as “pseudo-anonymous” because, while identities are hidden, transactions can still be traced. More privacy-focused cryptocurrencies, like Monero or Zcash, take additional measures to enhance user anonymity.
Global Access and Inclusion
Another transformative feature of blockchain in cryptocurrency is its ability to provide financial services to people around the world, especially those in underbanked or unbanked regions. Traditional banking systems are often inaccessible to large portions of the global population due to geographic, economic, or regulatory barriers.
Blockchain, however, is borderless. All someone needs to participate in the crypto economy is an internet connection. This has opened up financial opportunities to millions of people who were previously excluded from the traditional banking system, empowering them to store value, make transactions, and even access credit through decentralized finance (DeFi).
Blockchain’s Role in Enabling Smart Contracts
What Are Smart Contracts?
Blockchain technology has given rise to a new form of contract called “smart contracts.” These are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. Smart contracts automatically enforce the agreement when certain conditions are met, eliminating the need for intermediaries.
For example, a smart contract could be used to facilitate the transfer of a cryptocurrency token once certain criteria are met, such as the completion of a project or the fulfillment of a service. This automation reduces the risk of fraud, speeds up transactions, and cuts down costs.
How Smart Contracts Impact Crypto
Smart contracts have become a crucial component of blockchain ecosystems, especially in cryptocurrencies like Ethereum. They enable decentralized applications (dApps) to operate autonomously, from lending platforms to decentralized exchanges (DEXs). By removing the need for third parties, smart contracts increase efficiency, reduce costs, and make blockchain systems more trustworthy.
Blockchain and Crypto Mining
How Mining Works
In the world of cryptocurrencies, mining refers to the process by which transactions are validated and added to the blockchain. In proof-of-work (PoW) systems like Bitcoin, miners use computational power to solve complex mathematical problems. Once they solve these problems, they get the right to add a new block of transactions to the blockchain.
Mining not only validates transactions but also creates new coins. Miners are rewarded with cryptocurrency for their efforts, which incentivizes people to participate and secure the network.
Blockchain Incentivizing Miners
Blockchain plays a key role in motivating miners by providing a system of rewards. This is especially true for proof-of-work systems, where miners compete to solve complex problems. The first one to solve it gets to add the block and receive a reward, usually in the form of newly minted cryptocurrency.
This process ensures that transactions are securely validated and that the network remains decentralized and trustworthy. Without the blockchain’s incentivization model, many cryptocurrencies wouldn’t be able to function as efficiently or securely as they do.
Future of Blockchain in Crypto
Scalability and Innovation
As blockchain continues to grow in popularity, one of its biggest challenges is scalability. Blockchains like Bitcoin and Ethereum, in their current form, can only handle a limited number of transactions per second. This has led to network congestion and high transaction fees during periods of high demand.
However, innovations like layer 2 solutions, sharding, and the transition to proof-of-stake (PoS) are being developed to increase blockchain scalability. These improvements will allow blockchain networks to handle more transactions, reduce costs, and expand their use cases beyond just cryptocurrencies.
Potential Use Cases
Blockchain’s potential extends far beyond cryptocurrency. We’re already seeing it being used in industries like supply chain management, healthcare, and digital identity. But in the context of crypto, blockchain will likely continue to play a pivotal role in the development of decentralized finance (DeFi), non-fungible tokens (NFTs), and tokenized assets.
As blockchain technology evolves, its role in the crypto space will only grow. It will enable more complex applications, foster greater financial inclusion, and drive new innovations in how we store, transfer, and manage value.
Conclusion
Blockchain is the backbone of cryptocurrency, providing the infrastructure that makes decentralized digital currencies possible. Its role in securing transactions, fostering transparency, and enabling innovative financial applications is invaluable. As blockchain technology continues to evolve, its impact on the crypto world will expand, offering new opportunities and shaping the future of finance.







