The internet has come a long way, evolving from a static information-sharing platform to an interactive hub, and now to a decentralized, autonomous ecosystem. Web3 is at the forefront of this evolution, promising a future where users have more control, transparency, and security. But what exactly is a decentralized autonomous ecosystem, and how does it shape our digital future? Let’s dive in to explore this revolutionary concept.
What is Web3? 
Web3 represents the third generation of the internet, building on the foundations of its predecessors.
- Web1: The early days of the internet were defined by static websites with read-only access. Users could consume information but had limited interaction.
- Web2: With platforms like Facebook and Google, the web became interactive. However, centralized platforms controlled user data and decision-making.
Web3 flips the script by decentralizing control and ownership, powered by blockchain technology. It’s an internet where users are not just participants but stakeholders.
Unlike Web2, where a few corporations control data and platforms, Web3 envisions a peer-to-peer network where users have ownership, governance, and autonomy.
Understanding Decentralized Autonomous Ecosystems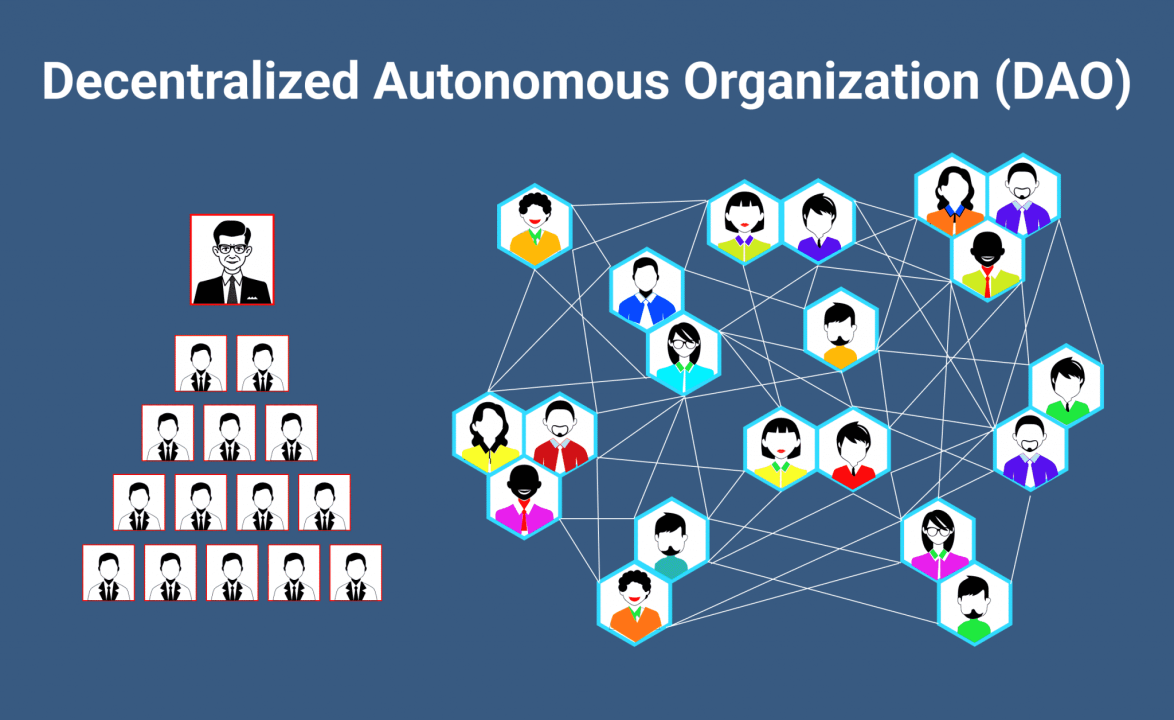
In simple terms, a decentralized autonomous ecosystem is a system where decisions are made without a central authority. Instead, it leverages blockchain technology, smart contracts, and community participation to operate autonomously.
At its core are Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs)—entities that function based on rules encoded in smart contracts. These ecosystems thrive on transparency, immutability, and community-driven governance.
Key Components of Web3’s Autonomous Ecosystem
To fully grasp how this ecosystem operates, let’s break down its main components:
1. Blockchain Technology
Blockchain serves as the backbone of Web3. It’s a distributed ledger that records transactions transparently and securely. Consensus mechanisms, like Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS), ensure network integrity.
For example, Ethereum and Solana are popular blockchains supporting decentralized ecosystems, enabling everything from financial transactions to smart contracts.
2. Smart Contracts
Smart contracts are self-executing programs stored on the blockchain. They automatically enforce agreements when pre-defined conditions are met.
For instance, in a DAO, a smart contract might trigger a funding release once a proposal gains enough votes. This eliminates the need for intermediaries, reducing delays and costs.
3. Tokens and Cryptocurrencies
Tokens are the lifeblood of decentralized ecosystems. They facilitate governance, rewards, and access to various services.
- Utility Tokens: Allow users to interact with a specific application or platform.
- Governance Tokens: Grant holders voting rights in a DAO, giving them a say in the ecosystem’s future.
4. Decentralized Applications (DApps)
DApps are software applications built on blockchain. Unlike traditional apps, they run on decentralized networks, ensuring greater transparency and security.
Examples include Uniswap (a decentralized exchange) and Axie Infinity (a blockchain-based game).
Benefits of a Decentralized Autonomous Ecosystem
Web3’s decentralized autonomous ecosystems offer a host of advantages:
1. User Empowerment
In Web3, users own their data, wallets, and digital assets. This shifts power from corporations to individuals.
2. Transparency and Trust
All transactions and activities are recorded on the blockchain, fostering transparency. Participants can verify processes without relying on third-party assurances.
3. Efficiency and Cost Savings
By automating processes through smart contracts, these ecosystems reduce reliance on intermediaries, saving time and resources.
4. Resilience
Decentralization eliminates single points of failure, making systems more robust against attacks or outages.
Challenges in Building a Decentralized Ecosystem
While the potential is immense, Web3’s autonomous ecosystem faces several hurdles:
1. Scalability
Blockchain networks often struggle with transaction speeds and scalability, particularly during peak demand. Solutions like layer-2 scaling aim to address this, but it remains an ongoing challenge.
2. Regulatory Uncertainty
Governments are still catching up with the implications of decentralization. Navigating compliance without compromising autonomy is a tightrope walk.
3. User Adoption
Despite its promise, Web3 can be complex for non-technical users. Simplifying interfaces and educating users is essential for broader adoption.
Real-World Applications of Web3’s Autonomous Ecosystem
The decentralized autonomous ecosystem isn’t just a concept; it’s already transforming industries:
1. Finance
Decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms like Compound and Aave allow users to lend, borrow, and trade without intermediaries.
2. Governance
DAOs, such as MakerDAO, let communities govern platforms democratically, ensuring decisions align with user interests.
3. Gaming
Blockchain games like Decentraland offer play-to-earn models, creating digital economies where players own in-game assets.
4. Data Privacy
Decentralized identity systems, like those offered by projects like SelfKey, allow users to control their personal information.
The Future of Web3 and Decentralized Ecosystems
As Web3 continues to evolve, its decentralized autonomous ecosystem holds the potential to reshape not just the internet but entire industries.
- Increased Adoption: Expect more mainstream companies to integrate Web3 principles.
- Technological Advancements: Innovations in scalability and user experience will address current limitations.
- Industry Transformation: Beyond tech, industries like healthcare, education, and supply chain management will leverage Web3’s autonomy and transparency.
Conclusion
Web3’s decentralized autonomous ecosystem is more than a technological shift—it’s a paradigm change. By empowering users, promoting transparency, and reducing dependence on central authorities, it paves the way for a more equitable digital world.
As this ecosystem matures, the opportunities for individuals and businesses to participate are boundless. Whether it’s exploring DAOs, engaging with DApps, or simply learning more, the future is decentralized, and it’s yours to shape.







