The internet as we know it has been evolving rapidly, and the next big shift is happening right in front of us. Web3, the decentralized version of the web, is gaining momentum as users begin to demand more control, privacy, and transparency. At the heart of this transformation is the decentralized network—the foundation that makes Web3 possible. In this blog, we’ll explore how decentralized networks are reshaping the way we interact with the internet, putting power back into the hands of users.
What is a Decentralized Network?
To understand how decentralized networks are transforming Web3, it’s essential to first grasp what a decentralized network is. In simple terms, a decentralized network is a system where data and resources are distributed across multiple nodes, rather than relying on a single central server. This structure differs from traditional centralized systems where control is in the hands of one authority or organization.
In centralized systems, data is stored and controlled by companies like Google, Facebook, or Amazon. These companies can access, control, or even restrict your data. In contrast, a decentralized network removes the middleman, giving control back to the users. Information is spread across multiple nodes, meaning no single entity has absolute power over the system.
Understanding Web3
Web3 represents the next evolution of the internet, shifting away from the centralized model of Web2. While Web2 is dominated by large corporations controlling platforms, Web3 aims to create a more open, transparent, and user-owned internet.
Built on blockchain technology, Web3 decentralizes everything from data storage to transaction verification. The primary goal of Web3 is to empower users to take ownership of their data, identity, and online assets. With blockchain at its core, Web3 offers a system where trust is maintained through code and cryptography rather than relying on corporations.
How Decentralized Networks are Powering Web3
Data Ownership
One of the key elements of Web3 powered by decentralized networks is data ownership. In today’s Web2 world, users give up their personal data in exchange for free services. However, in Web3, decentralized networks allow users to have full control over their data. Through blockchain technology, users can store their data securely without relying on centralized platforms, meaning they decide who has access to their information.
No Single Point of Failure
In a decentralized network, there is no single point of failure. Unlike centralized systems where a server crash can take down a website or app, decentralized networks spread data across multiple nodes. If one node goes down, others remain active, ensuring the system keeps running smoothly. This makes Web3 more resilient to outages, censorship, or hacking attempts, making it a more reliable alternative to today’s internet.
Transparency and Security
Decentralized networks bring transparency to Web3 because all transactions and data are recorded on a blockchain, a public and immutable ledger. This means anyone can verify actions on the network, ensuring transparency and accountability. Additionally, decentralized networks provide enhanced security through cryptographic methods, reducing the risk of data breaches or unauthorized access.
Decentralized Applications (dApps) and Their Role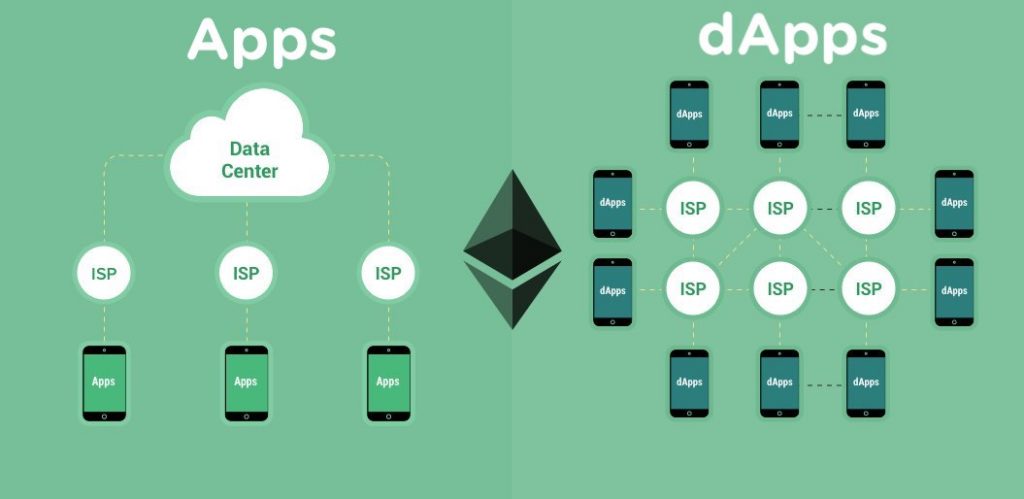
The decentralized nature of Web3 has given rise to decentralized applications, or dApps. These are applications that run on decentralized networks, often powered by blockchain technology like Ethereum. Unlike traditional apps, dApps are not controlled by any single entity and run on a peer-to-peer network.
Examples of dApps include platforms for decentralized finance (DeFi) like Uniswap, decentralized storage solutions like IPFS, and blockchain-based games. These dApps are changing how industries like finance, gaming, and social media operate by offering censorship-resistant platforms where users have greater control over their data and transactions.
Benefits of Decentralized Networks in Web3
Privacy and Security
A major advantage of decentralized networks in Web3 is the enhanced privacy they offer. In centralized systems, users’ data can be mined and exploited for profit. However, in a decentralized network, data is encrypted and stored across multiple nodes, meaning only the user controls access. This offers greater security and privacy in online interactions, making users less vulnerable to breaches or misuse of their data.
Resilience
Resilience is another key benefit of decentralized networks. Because data and resources are spread across numerous nodes, the system is much more resistant to failure. In a centralized system, if the main server goes down, the entire system crashes. But in a decentralized system, even if a few nodes fail, the network remains operational, providing a more robust and reliable infrastructure.
Empowering Users
Most importantly, decentralized networks give power back to the users. In Web3, users are no longer passive participants but active owners of their digital assets, data, and identities. Through decentralized networks, users can interact directly with one another, bypassing the need for intermediaries or central authorities.
Challenges of Decentralized Networks
Scalability
Despite its benefits, decentralized networks face challenges, one of the biggest being scalability. As more users join a decentralized network, maintaining performance can become difficult. Blockchain technology is particularly prone to this issue, as it can handle only a limited number of transactions per second compared to centralized systems like Visa or Mastercard.
Energy Consumption
Another concern is energy consumption. Many decentralized networks rely on blockchain technology, and some, like Bitcoin, use proof-of-work consensus mechanisms that require massive amounts of energy. While newer consensus models like proof-of-stake aim to reduce this energy demand, it remains a point of contention in discussions around decentralization.
User Adoption
A final challenge is user adoption. While Web3 offers numerous benefits, it’s still in its early stages, and the majority of internet users are unfamiliar with concepts like blockchain, dApps, or decentralized networks. Educating users and making decentralized systems more accessible will be critical for Web3’s growth.
The Future of Web3 with Decentralized Networks
Looking ahead, decentralized networks have the potential to revolutionize the internet as we know it. As technology improves, many of the current challenges—such as scalability and energy consumption—will likely be addressed. Innovations like Layer 2 solutions and more energy-efficient consensus mechanisms will make decentralized networks more scalable and sustainable.
The future of Web3 is one where users control their data, applications run independently of centralized authorities, and online interactions are more transparent and secure. As decentralized networks continue to grow, they will play a crucial role in shaping this new, more democratic internet.
Conclusion
Decentralized networks are transforming Web3 by providing a more secure, private, and user-controlled internet. From enabling data ownership to supporting dApps, decentralized networks are at the core of Web3’s mission to reshape how we interact online. While challenges like scalability and energy consumption remain, the potential for decentralized networks to power the future of the internet is undeniable. As we move toward this future, Web3 and decentralized networks promise to make the internet a more open and empowering place for all users.