Blockchain technology is reshaping industries globally, and supply chain management is no exception. With its unique ability to enhance transparency, traceability, and security, blockchain has the potential to overcome many challenges that traditional supply chains face. From food and agriculture to pharmaceuticals and luxury goods, blockchain is making a transformative impact across diverse sectors. Let’s dive into how blockchain-powered supply chains work, their benefits, real-world applications, and the challenges ahead.
Introduction to Blockchain in Supply Chain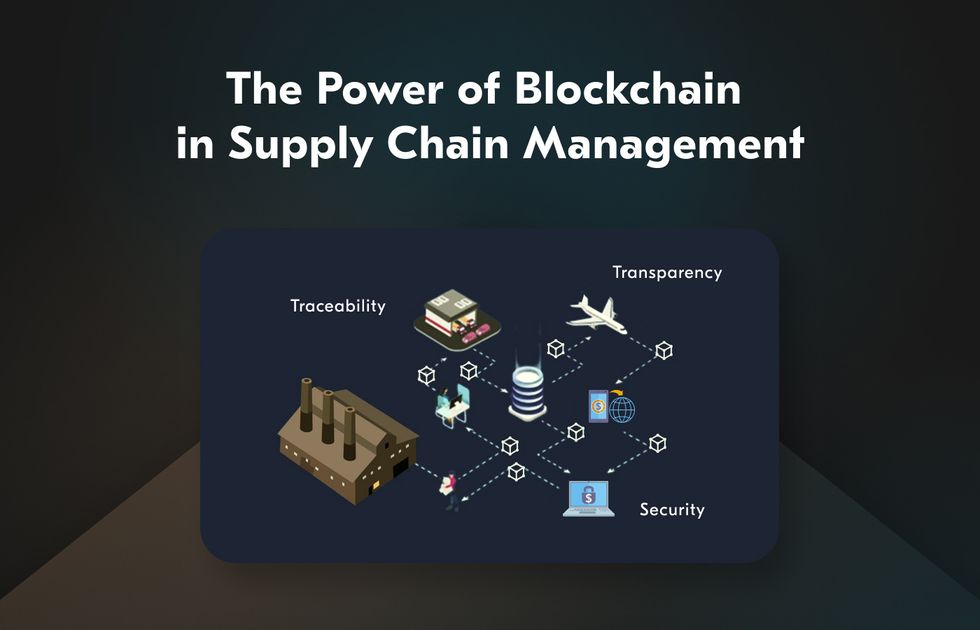
Blockchain is often associated with cryptocurrencies, but its application extends far beyond digital assets. In simple terms, blockchain is a decentralized ledger system where data is stored across multiple computers in a way that’s secure, transparent, and nearly impossible to alter. For supply chains, which involve numerous stakeholders, transactions, and exchanges, blockchain offers a way to address many inefficiencies and visibility issues.
Why Blockchain?
In today’s globalized economy, traditional supply chains face a range of challenges—from tracking inventory to ensuring product authenticity. Problems like lack of visibility, delays, counterfeiting, and data tampering can lead to financial losses and reputational damage. Blockchain technology addresses these by providing a single, transparent source of truth, helping build trust and efficiency across the supply chain.
Key Benefits of Blockchain in Supply Chain
Blockchain offers a suite of benefits that make it ideal for supply chain management:
- Enhanced Transparency: With a blockchain ledger, all participants in the supply chain can access a single source of data. This transparency allows stakeholders to track goods as they move through the supply chain, reducing disputes and improving collaboration.
- Improved Traceability: Blockchain’s traceability helps verify the origin of products. From tracking food from farms to grocery stores to verifying the source of luxury goods, traceability is essential for quality assurance and accountability.
- Strengthened Security: Blockchain records are highly secure and resistant to tampering. Each transaction is encrypted and stored in a decentralized network, making it nearly impossible to alter records without detection.
- Efficient Data Management: With blockchain, data management becomes seamless and real-time, enabling faster decision-making and reducing paperwork.
- Cost Savings: By cutting down the need for intermediaries and reducing errors, blockchain can lead to significant cost savings over time.
How Blockchain Technology Works in Supply Chains
The main principles of blockchain make it an ideal fit for supply chain processes:
- Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT): Blockchain’s decentralized structure allows for a single, verified record of all transactions accessible to everyone on the network. This prevents data discrepancies and keeps everyone on the same page.
- Smart Contracts: These are self-executing contracts that automatically trigger actions when pre-set conditions are met. In supply chains, smart contracts can streamline processes like payment release upon delivery or order confirmation, reducing the need for intermediaries.
- Tokenization and Digital Assets: Tokens in a blockchain supply chain can represent assets, including raw materials, inventory, or completed goods. This enables seamless tracking and transfers between stakeholders.
- IoT Integration: Pairing blockchain with IoT devices allows for precise tracking of products, as IoT sensors can record data (like temperature or location) directly onto the blockchain, ensuring accurate and timely information.
Real-World Applications of Blockchain in Supply Chains
Blockchain-powered supply chains are proving valuable in a variety of industries:
- Food and Agriculture: Blockchain enhances food safety by tracking products from farm to table. Consumers and companies can verify a product’s source, ensuring freshness and quality. For example, IBM’s Food Trust project with Walmart helps track produce, improving safety and reducing waste.
- Pharmaceuticals: Counterfeit drugs are a huge issue in the pharmaceutical industry. Blockchain allows verification of every stage in the distribution process, ensuring authenticity and compliance.
- Retail and Luxury Goods: Blockchain helps retailers and luxury brands combat counterfeiting by verifying product origin. Brands like Louis Vuitton and De Beers have started using blockchain to ensure authenticity and protect brand integrity.
- Automotive Industry: Blockchain can streamline the automotive supply chain, from parts tracking to ensuring ethical sourcing of materials. It enhances inventory tracking and helps ensure regulatory compliance.
- Electronics and Tech: Blockchain can confirm the ethical sourcing of materials and provide transparency in the assembly process, ensuring quality and reducing the risk of counterfeit components.
Companies Using Blockchain in Supply Chains
Many companies are already harnessing blockchain’s potential for supply chains:
- Walmart and IBM Food Trust: Walmart partnered with IBM to create a blockchain-powered system for tracking produce. The system allows Walmart to trace food items back to their origin in seconds, improving safety and transparency.
- Maersk and TradeLens: Shipping giant Maersk developed TradeLens, a blockchain platform for global shipping. It helps track cargo, streamline documentation, and enhance collaboration, reducing processing times and costs.
- De Beers’ Tracr Platform: De Beers uses the Tracr platform to track diamonds from mine to retail, ensuring that diamonds are conflict-free and ethically sourced.
These case studies highlight how companies are adopting blockchain to enhance transparency, efficiency, and trust in their supply chains.
Challenges and Considerations for Adopting Blockchain in Supply Chains
While blockchain holds promise, it’s not without challenges:
- Implementation Costs: The initial cost of implementing blockchain technology can be high, especially for smaller businesses. Blockchain requires technical expertise and infrastructure changes, which can be prohibitive.
- Integration with Legacy Systems: Many companies already have complex, established supply chain systems. Integrating blockchain with existing systems can be challenging and time-consuming.
- Data Privacy and Confidentiality: Some supply chain information is confidential. While blockchain’s transparency is a strength, companies need to balance it with data privacy concerns.
- Regulatory and Compliance Issues: Blockchain is still a developing technology, and its use is regulated differently around the world. Companies need to navigate various compliance requirements based on their region and industry.
- Industry-Wide Standards: The lack of unified standards across industries can limit blockchain’s effectiveness. Collaboration is needed to establish interoperable solutions that can work across borders.
The Future of Blockchain in Supply Chain Management
Blockchain has the potential to play an even larger role in supply chains in the future:
- Growth Potential: As the technology matures, we can expect more companies to adopt blockchain for supply chain management. This trend will likely accelerate as blockchain solutions become more affordable and scalable.
- Emerging Trends: New technologies, such as AI and machine learning, will likely integrate with blockchain, further enhancing supply chain efficiency. Interoperability between blockchain networks is also on the rise, which will simplify collaboration across different blockchain platforms.
- Widespread Adoption: As awareness of blockchain’s benefits grows, it’s likely to become a standard tool in supply chain management, especially for industries that require strict quality control and transparency.
Conclusion
Blockchain-powered supply chains offer a new level of transparency, efficiency, and security, providing companies with a competitive advantage. By allowing participants to access a shared, immutable ledger, blockchain technology improves accountability, ensures traceability, and minimizes the risk of fraud. While there are challenges in adopting blockchain, such as high costs and regulatory uncertainties, the potential benefits far outweigh these hurdles.
As blockchain technology continues to develop, its impact on supply chain management will only increase, potentially revolutionizing the industry and setting a new standard for transparency and trust in global commerce. Blockchain isn’t just a trend; it’s the future of supply chains.







